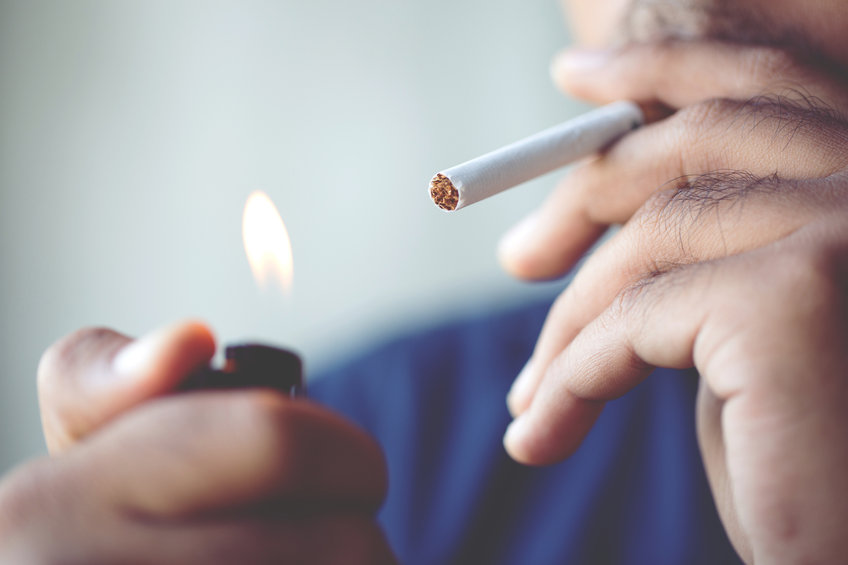


About 90% of lung cancer is caused by cigarette smoking. Tobacco smoke contain carcinogens that can initiate tumor development. Tobacco smoke can also weaken the body’s immune system and caner surveillance mechanisms. In addition to lung cancer, cigarette smoking has been associated with almost every type of cancer in the body.
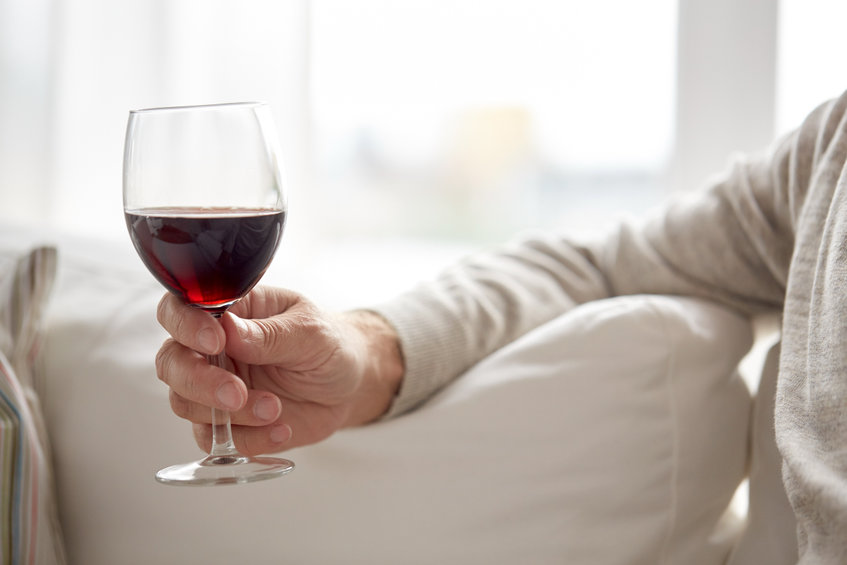
Alcohol consumption is a major risk factor for oral and oropharyngeal cancer as well as liver cancer. Alcohol consumption has also been associated with esophageal, breast, and colon cancer.
About 15-20% of total cancer cases globally can be attributed to infections, including H. pylori (stomach), hepatitis B and C (liver), herpes (Kaposi’s sarcoma), HIV(lymphoma, Kaposi’s sarcoma), and HPV (cervix, anus, throat, penis, vagina). Infection-associated cancer can be prevented through vaccination and screening.
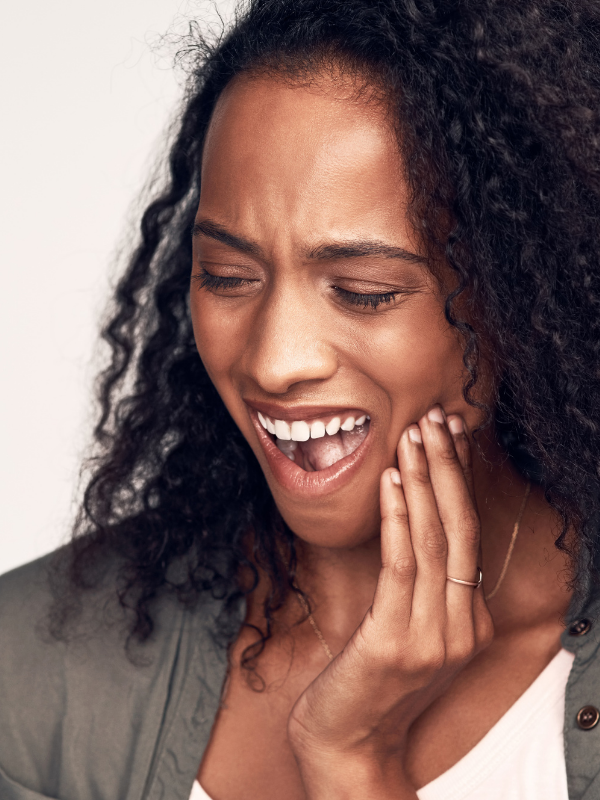

The risks of developing oral cancer can be reduced if individuals avoid tobacco use, heavy alcohol drinking, and reduce their exposure to oral HPV infections.
Oral cancer is preceded by precancerous lesions.
Detection, and treatment of these precancerous lesions can prevent the development of oral cancer
The risks of developing oral cancer can be reduced if individuals avoid tobacco use, heavy alcohol drinking, and reduce their exposure to oral HPV infections.
Oral cancer is preceded by precancerous lesions.
Detection, and treatment of these precancerous lesions can prevent the development of oral cancer
Please wait while flipbook is loading. For more related info, FAQs and issues please refer to DearFlip WordPress Flipbook Plugin Help documentation.

