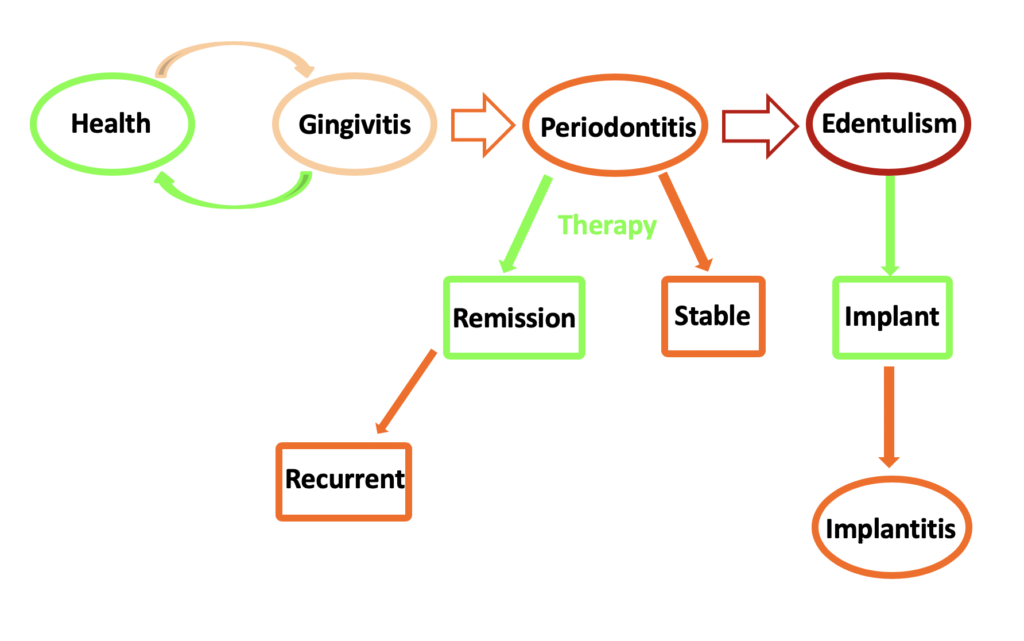
Periodontal disease is chronic inflammation of the periodontium surrounding the teeth, If left untreated, this inflammation could lead to destruction of the periodontal ligament and supporting bone, and ultimately tooth loss. It is estimated that up to 75% of tooth loss in adults is due to periodontal disease.
Gingivitis is the mildest form of periodontal disease, and is characterized by gingival redness and edema, but the absence of periodontal attachment loss. Gingivitis is reversible with professional treatment and proper home teeth cleaning techniques. However, in some individuals, gingivitis may progress to periodontitis, which is characterized by periodontal attachment loss, bone loss, movement of the teeth, and tooth loss.
Overall, periodontal disease is caused by overgrowth of harmful oral bacteria species, which reflects an imbalance of the oral microbiome community: a shift from health-associated bacterial species to periodontitis-associated bacterial species.